Our skin is more than just a protective layer—it reflects our overall health, lifestyle, and well-being. Yet, many people struggle with common skin conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis, which can affect confidence, comfort, and quality of life. Understanding the causes, management strategies, and the supportive role of antioxidants can help you take better care of your skin.
- Acne: More Than Just Pimples
What it is:
Acne occurs when hair follicles are clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria, causing pimples, blackheads, or cysts. While common in teenagers, adults can also experience acne due to hormonal changes, stress, diet, or genetics.
Management:
- Topical treatments: Benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and retinoids help unclog pores and reduce inflammation.
- Oral medications: Antibiotics or hormonal therapy may be used for moderate to severe acne.
- Lifestyle habits: Gentle cleansing, avoiding picking or squeezing pimples, and maintaining a balanced diet.
- Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E, and green tea polyphenols help calm inflammation, reduce redness, and support healing of post-acne marks. While not a primary treatment, they enhance skin recovery and reduce oxidative stress that contributes to acne.
- Eczema: Soothing Itchy, Inflamed Skin
What it is:
Eczema (atopic dermatitis) is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by itchy, dry, and red patches. It often results from a weakened skin barrier and an overactive immune response.
Management:
- Moisturization: Thick emollients restore the skin barrier and lock in moisture.
- Medications: Topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors manage flare-ups.
- Avoid triggers: Harsh soaps, allergens, and extreme weather can worsen symptoms.
- Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E, along with flavonoids from plant-based sources, help protect skin cells from oxidative stress, strengthen the skin barrier, and may reduce the severity and frequency of flare-ups.
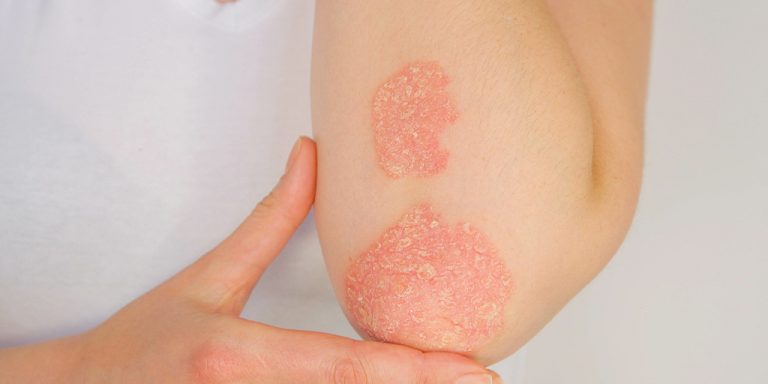
- Psoriasis: When Skin Turns Over Too Fast
What it is:
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition where the immune system accelerates skin cell turnover, leading to thick, scaly patches. Commonly affected areas include elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
Management:
- Topical treatments: Steroid creams and vitamin D analogs reduce inflammation and scaling.
- Phototherapy: Controlled UV exposure can calm the overactive immune response.
- Systemic treatments: Oral or injectable medications for moderate to severe cases.
- Antioxidants: Selenium, vitamin E, and polyphenols may help reduce oxidative damage and support overall skin health. While antioxidants alone cannot control psoriasis, they can complement standard treatments and help improve skin resilience.
General Skin Health Tips
- Gentle cleansing and regular moisturization to maintain a healthy skin barrier.
- Sun protection: Broad-spectrum sunscreen prevents damage and flare-ups.
- Healthy lifestyle: Balanced diet, hydration, stress management, and adequate sleep.
- Antioxidant-rich foods: Berries, nuts, green tea, and colorful vegetables help reduce oxidative stress and protect skin cells.
- Consult a dermatologist: For persistent or severe symptoms, professional guidance is essential.
Takeaway:
Acne, eczema, and psoriasis can be challenging, but a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and antioxidant support can make a real difference. Antioxidants—both in diet and skincare—play a supportive role by reducing oxidative stress, calming inflammation, and helping the skin heal faster, even if their effect is minor compared to primary treatments. By understanding your skin and managing it scientifically, you can achieve healthier, more resilient skin over time.